Advent of British
- Next Europeans who came to India were English. This had a lengthy stay in India and of late ruled India.
- 31/12/1600 a group of merchants started a private company called ' English East India Company ' (nicknamed as John Company) to trade with India and eastern countries.
- Queen Elizabeth, I passed a charter on the same day stating that complete monopoly rights were given to East India Company over eastern trade for a period of 15 years. However, it was modified in 1609 by 'James I' successor of 'Elizabeth I' stating that monopoly period was extended indefinitely and this remains till further Royal orders. This monopoly remained till 1813.
- Initial English setups in India
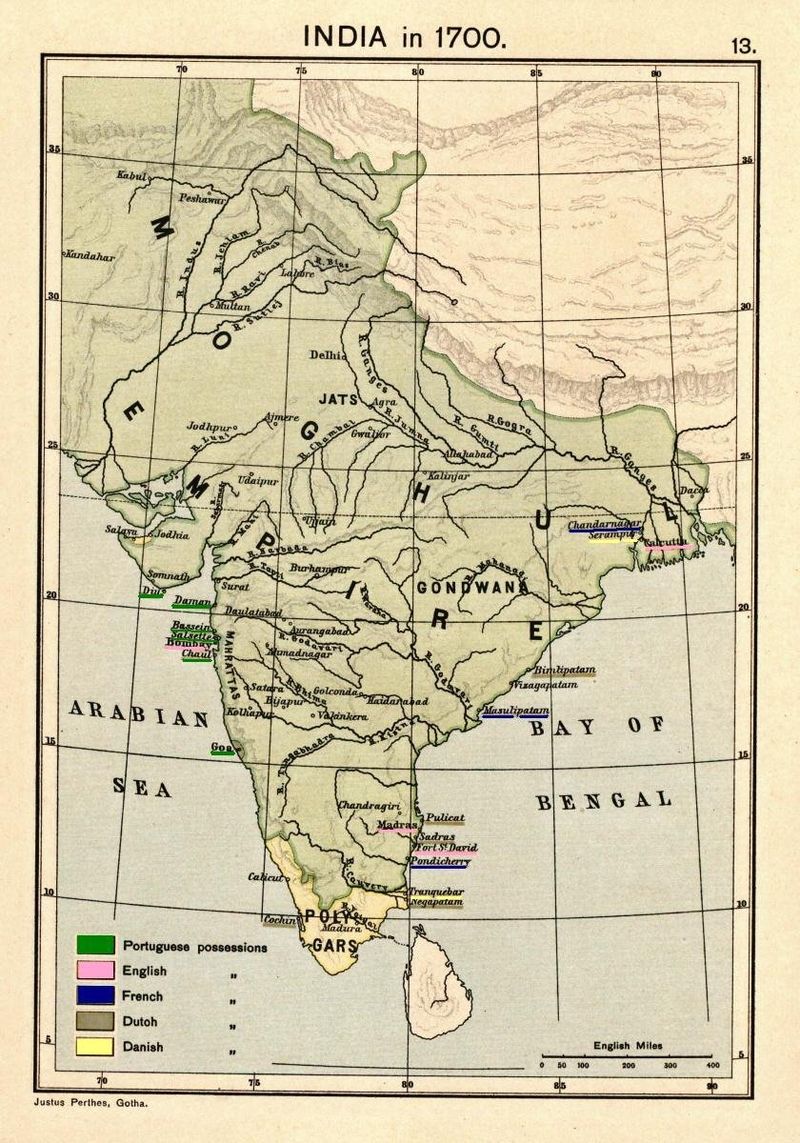
- Surat in 1608 was the first settlement.
- Machilipatnam, Andhra Pradesh in 1611 was first settlement in Eastern Coast and many other settlements later.
- Unlike the earlier Europeans British came with a different strategy. As part of this, they established a headquarter each at Bombay, Madras and Calcutta. Each headquarter has its own governor and own territorial jurisdiction.
- Initially, governors were independent of each other. Everyone has his own trade and headache. But after some time this caused a chaos so Kolkata governor was made as Governor General and other two governors were brought under his administration. Governor General Office was first made in 1773 and 'Warren Hastings' was first governor general.
- Construction of Cities
- Madras :— In the year, 1639 site of Madras was procured by a British officer 'Francis De' from Venkatadri Naidu, a local officer in this territory. This city was named as Chennapatnam (after Venkatadri Naidu's father Chennappa) and eventually changed to Madras and now to Chennai again. British built a fort called 'St. George Fort'.
- Bombay :— In the year 1668 site of Bombay ay was given to 'Gerald Aungier' by British King 'John II' (In 1661 there was a marriage ceremony of Portuguese Princess 'Catherine Briganza' and British King 'Charles II' and as part of marriage dowry Bombay was given to King 'Charles II'. King 'John II' was successor so he inherited Bombay).
- Calcutta : — In the year 1690 a British officer 'Jab Chornock' purchases 3 villages in Bengal from Mughal Sultan 'Aurangzeb'. These 3 villages were merged into one to develop a city called Calcutta. Here they built a fort called 'Fort William' Seat of Calcutta governor is in this fort so it is called 'Governor of Fort William'. The villages merged were Govindpur, Kalikata and Satnauti.